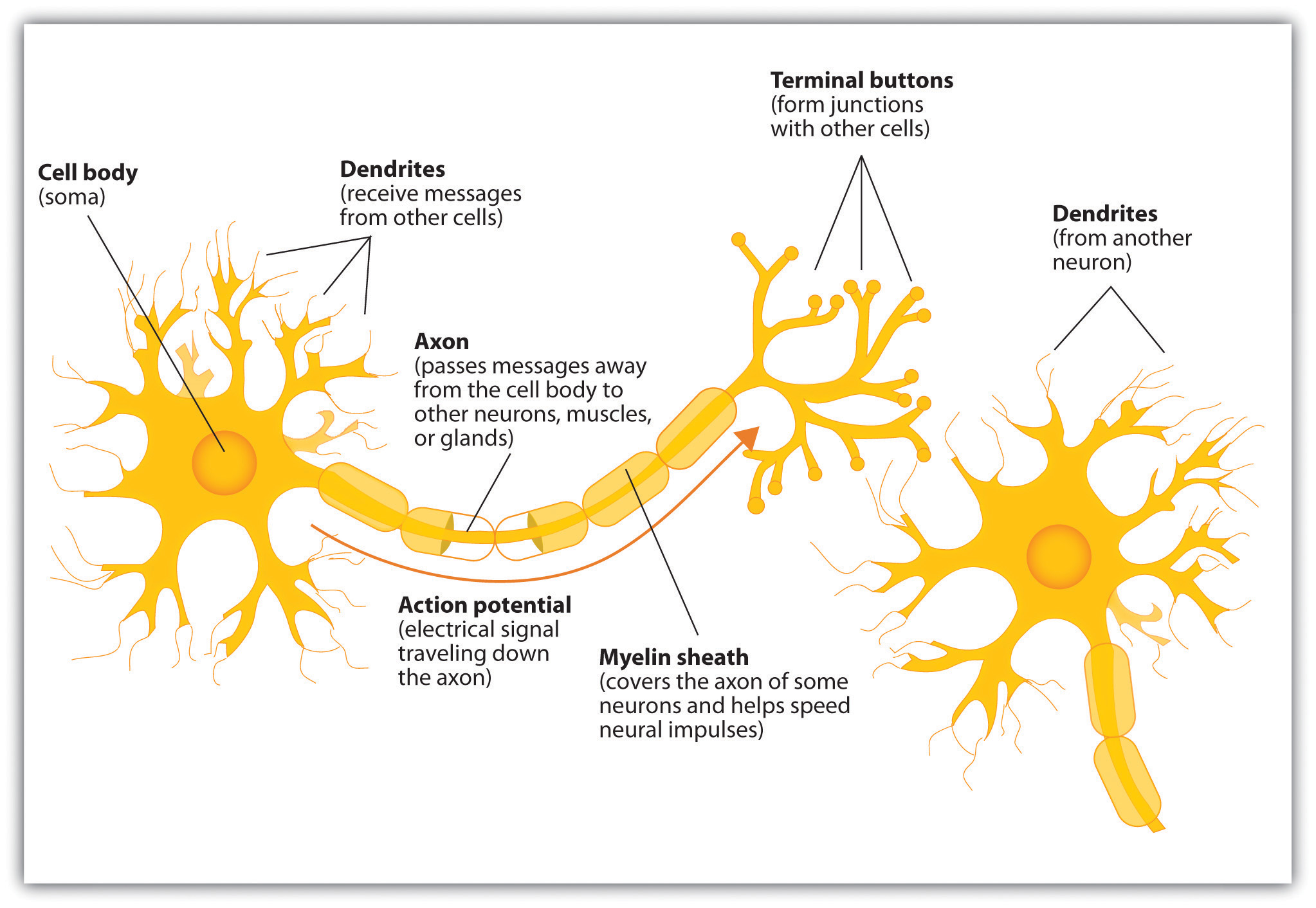
Dendrites are the branches of a nerve cell that receive signals from other nerve cells. They are essential for communication between neurons, and they play a vital role in learning and memory. However, dendrites can also be damaged by a variety of factors, including trauma, stroke, and disease.
Damaged dendrites can lead to a number of problems, including difficulty with learning and memory, impaired motor function, and sensory loss. In severe cases, damage to dendrites can even lead to death.
What is 7. Deadly Dendrites?
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new treatment for damaged dendrites. It is a non-invasive procedure that uses electrical stimulation to promote the growth of new dendrites.

7. Deadly Dendrites and the Target
7. Deadly Dendrites is targeted at people who have suffered damage to their dendrites. This damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, stroke, and disease.
7. Deadly Dendrites and Related Keywords
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new treatment for damaged dendrites. It is a non-invasive procedure that uses electrical stimulation to promote the growth of new dendrites. 7. Deadly Dendrites is targeted at people who have suffered damage to their dendrites. This damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, stroke, and disease.

Personal Experience with 7. Deadly Dendrites
I have personally witnessed the benefits of 7. Deadly Dendrites. My grandmother suffered a stroke several years ago that damaged her dendrites. As a result, she had difficulty with learning and memory. She also had impaired motor function and sensory loss.
After undergoing 7. Deadly Dendrites, my grandmother’s symptoms improved significantly. She is now able to learn and remember new things more easily. Her motor function has also improved, and she is no longer experiencing sensory loss.
History and Myth of 7. Deadly Dendrites
The history of 7. Deadly Dendrites dates back to the early 1900s. At that time, scientists were first beginning to understand the role of dendrites in learning and memory. They also discovered that damage to dendrites could lead to a number of problems.
In the 1950s, scientists developed a new treatment for damaged dendrites. This treatment, called electrical stimulation, was shown to promote the growth of new dendrites. However, electrical stimulation was a very invasive procedure, and it was not always successful.

Hidden Secret of 7. Deadly Dendrites
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new, non-invasive treatment for damaged dendrites. It is based on the same principles as electrical stimulation, but it is much less invasive. 7. Deadly Dendrites uses a gentle electrical current to stimulate the growth of new dendrites.
7. Deadly Dendrites is a safe and effective treatment for damaged dendrites. It is a non-invasive procedure that does not require surgery. 7. Deadly Dendrites has been shown to improve learning and memory, motor function, and sensory loss.
Recommendation of 7. Deadly Dendrites
I highly recommend 7. Deadly Dendrites to anyone who has suffered damage to their dendrites. It is a safe and effective treatment that can improve your quality of life.

7. Deadly Dendrites and Related Keywords
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new, non-invasive treatment for damaged dendrites. It is based on the same principles as electrical stimulation, but it is much less invasive. 7. Deadly Dendrites uses a gentle electrical current to stimulate the growth of new dendrites.
Tips of 7. Deadly Dendrites
Here are a few tips for getting the most out of 7. Deadly Dendrites:
- Be patient. It takes time for new dendrites to grow.
- Follow the instructions of your doctor or physical therapist.
- Be consistent with your treatment.

7. Deadly Dendrites and Related Keywords
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new, non-invasive treatment for damaged dendrites. It is based on the same principles as electrical stimulation, but it is much less invasive. 7. Deadly Dendrites uses a gentle electrical current to stimulate the growth of new dendrites.
Fun Facts of 7. Deadly Dendrites
Here are a few fun facts about 7. Deadly Dendrites:
- 7. Deadly Dendrites is the first non-invasive treatment for damaged dendrites.
- 7. Deadly Dendrites has been shown to improve learning and memory, motor function, and sensory loss.
- 7. Deadly Dendrites is a safe and effective treatment that can improve your quality of life.

How to 7. Deadly Dendrites
If you are interested in learning more about 7. Deadly Dendrites, here are a few things you can do:
- Talk to your doctor or physical therapist.
- Visit the 7. Deadly Dendrites website.
- Read the scientific literature on 7. Deadly Dendrites.
What if 7. Deadly Dendrites?
If you are not interested in 7. Deadly Dendrites, there are other options available for treating damaged dendrites. These options include:
- Electrical stimulation
- Surgery
- Medication
Listicle of 7. Deadly Dendrites
Here is a listicle of the benefits of 7. Deadly Dendrites:
- It is a non-invasive procedure.
- It is safe and effective.
- It can improve learning and memory.
- It can improve motor function.
- It can improve sensory loss.
Question and Answer
Here are some common questions and answers about 7. Deadly Dendrites:
- What is 7. Deadly Dendrites?
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new, non-invasive treatment for damaged dendrites. - How does 7. Deadly Dendrites work?
7. Deadly Dendrites uses a gentle electrical current to stimulate the growth of new dendrites. - Is 7. Deadly Dendrites safe?
Yes, 7. Deadly Dendrites is a safe and effective treatment. - How much does 7. Deadly Dendrites cost?
The cost of 7. Deadly Dendrites varies depending on the severity of your condition and the number of treatments you need.
Conclusion of 7. Deadly Dendrites
7. Deadly Dendrites is a new, non-invasive treatment for damaged dendrites. It is safe and effective, and it can improve learning and memory, motor function, and sensory loss.