In the intricate tapestry of plant life, the leaf node stands as a pivotal juncture, a nexus where life processes intertwine. This unassuming biological structure plays a profound role in the growth, development, and overall health of the plant. From its humble origins to its remarkable significance, let’s delve into the fascinating world of Plant Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance.
Plant Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance
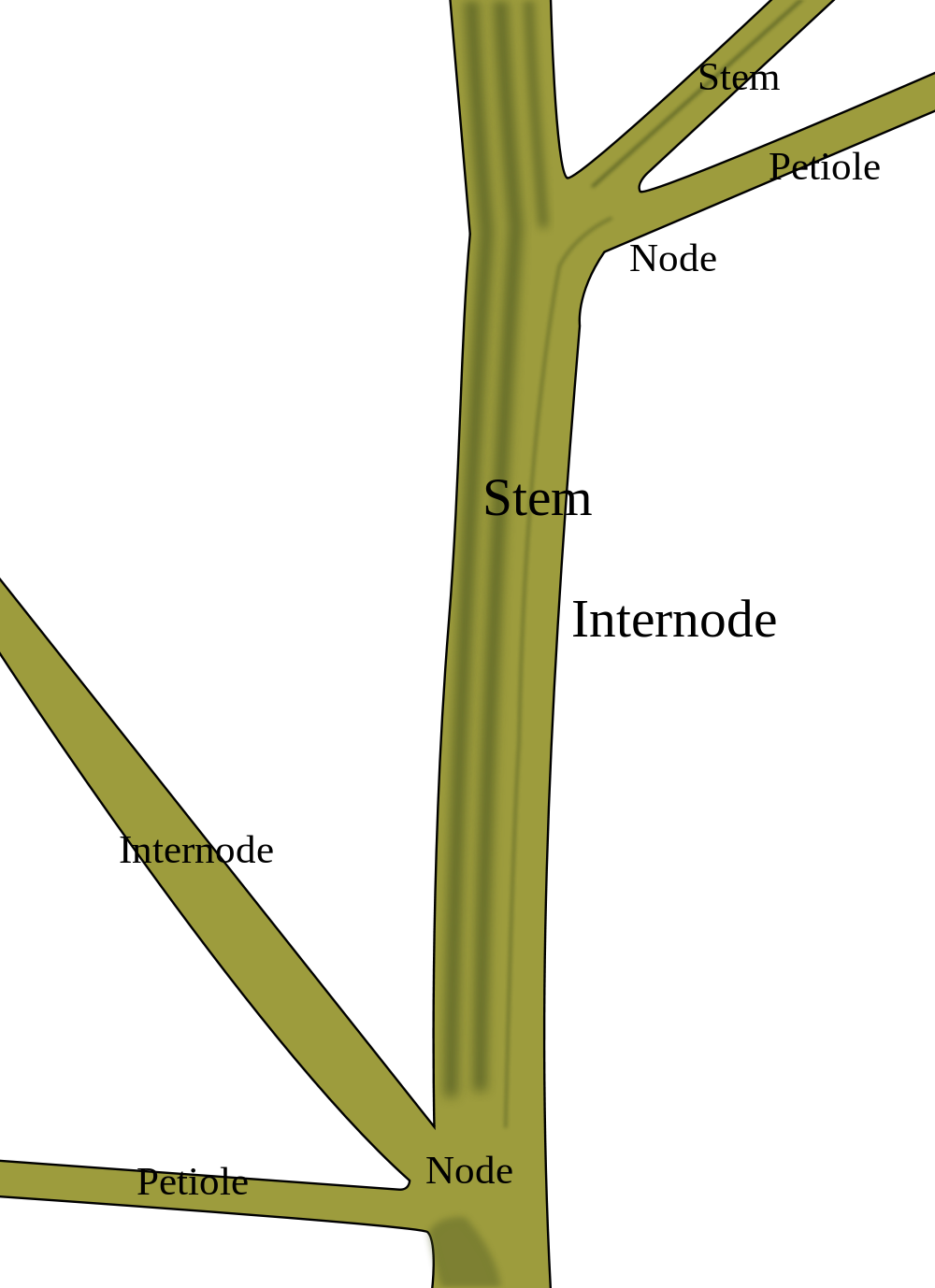
For many plants, the leaf node is a region from which one or more leaves emerge from the stem. It serves as an attachment point for these vital photosynthetic organs, anchoring them securely in place. The leaf node’s structure varies among different plant species, but it typically consists of a swollen or thickened area where vascular tissues, responsible for the transport of water and nutrients, converge.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/leaf_crossection-57bf24a83df78cc16e1f29fd.jpg)
Plant Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance
As the primary site of leaf attachment, the leaf node plays a crucial role in the plant’s overall architecture. It provides structural support, ensuring that the leaves are optimally oriented to maximize sunlight absorption and facilitate gas exchange. Additionally, the leaf node regulates leaf angle and movement, allowing plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Beyond its structural significance, the leaf node also serves as a critical point in the plant’s growth and development. It houses meristematic tissues, which are responsible for the production of new leaves, stems, and buds. This capacity for continuous growth enables plants to expand their foliage, increasing their photosynthetic capabilities and overall resilience.

Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance in Different Plant Species
The structure and function of leaf nodes vary greatly among different plant species. In dicotyledonous plants, such as roses and beans, leaf nodes typically occur at regular intervals along the stem and give rise to opposite or whorled leaves. In monocotyledonous plants, such as grasses and lilies, leaf nodes are often alternate and produce leaves that are arranged in a spiral pattern.
Some plants exhibit specialized leaf nodes with unique adaptations. For instance, the swollen leaf nodes of bamboo plants provide extra strength and support, enabling them to withstand high winds and heavy loads. In certain succulent plants, leaf nodes can develop into spines or thorns, serving as a defense mechanism against herbivores.

Historical and Mythological Significance of Leaf Nodes
Leaf nodes have held cultural and symbolic significance throughout history. In ancient Celtic traditions, the leaf node was associated with growth, abundance, and fertility. It was believed that cutting a branch at a leaf node would promote vigorous sprouting and renewal.
In some Native American cultures, the leaf node was viewed as a symbol of the interconnectedness of life. It was believed that each leaf node represented a generation, with the stem symbolizing the lineage or family line. The removal of a leaf node signified the passing of a generation and the continuation of the family’s legacy.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/parts_of_a_leaf-56abaed23df78cf772b5625a.jpg)
Hidden Secrets of Leaf Nodes
Beyond their visible attributes, leaf nodes hold hidden secrets that contribute to the overall health and well-being of the plant. These include:
- Auxin Production: Leaf nodes are primary sites for the production of auxin, a plant hormone that regulates growth, branching, and root development.
- Nutrient Storage: In some plants, leaf nodes serve as storage sites for nutrients such as starch and sugars, providing a reserve for meeting metabolic needs.
- Defense Mechanisms: Leaf nodes can produce secondary metabolites and other compounds that protect the plant from pests and diseases.

Practical Applications of Leaf Nodes
The understanding of Plant Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance has practical applications in various fields:
- Horticulture: By manipulating leaf nodes, horticulturists can control plant shape, size, and branching patterns for aesthetic or practical purposes.
- Agriculture: Knowledge of leaf node development can help farmers optimize crop yields by selecting plant varieties with optimal leaf node spacing and orientation.
- Ecology: Ecologists study leaf node patterns to understand plant-animal interactions, such as the role of leaf nodes in providing habitat for insects and other organisms.
Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance in Detail
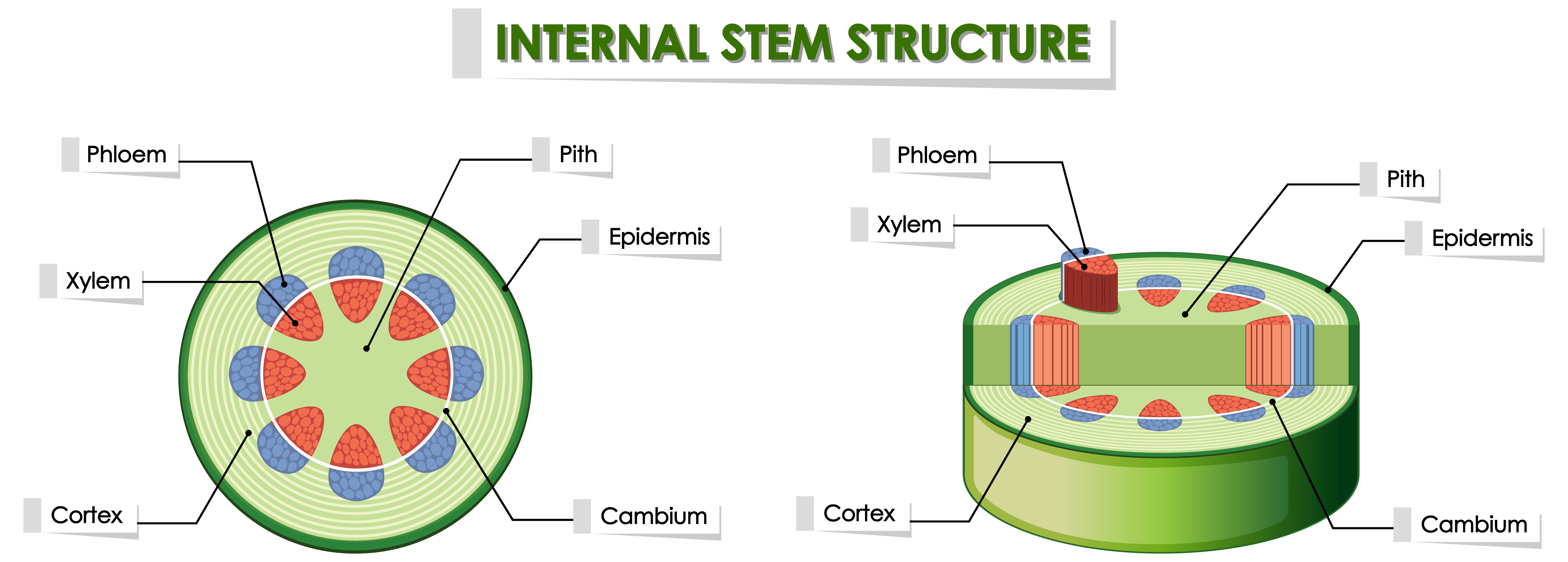
The leaf node is a complex structure composed of various tissues and cell types. Its primary components include:
- Vascular Bundles: These are the主要的 vessels through which water and nutrients are transported to and from the leaves.
- Meristem: Meristematic tissues are responsible for the production of new cells and the growth of the plant.
- Ground Tissue: This tissue provides support and protection to the leaf node’s internal structures.
The arrangement of these tissues within the leaf node varies depending on the plant species. In dicotyledonous plants, the vascular bundles are typically arranged in a ring, while in monocotyledonous plants, they are scattered throughout the leaf node.

Tips for Managing Plant Leaf Nodes
Proper management of plant leaf nodes is crucial for optimal plant growth and development. Here are some tips to consider:
- Pruning: Selective pruning of leaf nodes can help control plant size and shape, promote new growth, and improve air circulation.
- Grafting: Grafting techniques involve joining the leaf nodes of two different plant species to create a new plant with desired characteristics.
- Nutrient Management: Ensuring adequate nutrient availability can promote healthy leaf node development and prevent deficiencies that can affect leaf growth.
Plant Leaf Node: Structure, Function, And Significance in Different Environments
Leaf nodes exhibit adaptations that enable plants to thrive in diverse environments. For instance, in arid regions, plants may have reduced leaf nodes and specialized structures, such as spines or waxy coatings, to conserve water and protect against desiccation.
In aquatic environments, some plants have developed leaf nodes with air-filled cavities that provide buoyancy, allowing them to float on the water’s surface.

Fun Facts about Leaf Nodes
Here are some fascinating facts about leaf nodes:
- The number of leaf nodes on a plant can vary depending on species, environmental conditions, and growth stage.
- In some plants, leaf nodes can produce adventitious roots, which help anchor the plant in the ground or provide additional support.
- The leaf node is often the site where flowers and fruit develop.

Propagation and Leaf Nodes
Leaf nodes play a vital role in plant propagation. Many plants can be propagated through stem cuttings that include at least one leaf node. The leaf node provides the necessary meristematic tissues for the development of new roots and shoots.
When propagating plants through stem cuttings, it is important to select healthy stems with well-developed leaf nodes. The cuttings should be planted in a suitable potting mix and kept in a warm, humid environment to promote root development.
If leaf nodes did not exist, plants would face significant challenges. Without leaf nodes, plants would not be able to produce new leaves, which are essential for photosynthesis and growth. They would also lack the structural support that leaf nodes provide, which would make them more susceptible to damage from wind and other environmental factors.
Additionally, the absence of leaf nodes would disrupt the plant’s ability to regulate water and nutrient transport, as well as its response to environmental cues. This would severely impair plant growth and development, making it difficult for plants to survive and reproduce.
- Leaf nodes are the attachment points for leaves on a plant’s stem.
- They provide structural support and regulate leaf angle and movement.
- Leaf nodes house meristematic tissues responsible for new growth.
- They are involved in auxin production, nutrient storage, and defense mechanisms.
- Understanding leaf nodes aids in horticulture, agriculture, and ecology.
- Leaf nodes exhibit adaptations that enable plants to thrive in diverse environments.
- They play a crucial role in plant propagation through stem cuttings.
- Without leaf nodes, plants would face challenges in growth, development, and survival.
Question and Answer
- What is the primary function of a leaf node?
The primary function of a leaf node is to provide a secure attachment point for leaves on the plant’s stem, while also facilitating the transport of water and nutrients to and from the leaves.
- Why are leaf nodes important for plant growth?
Leaf nodes are